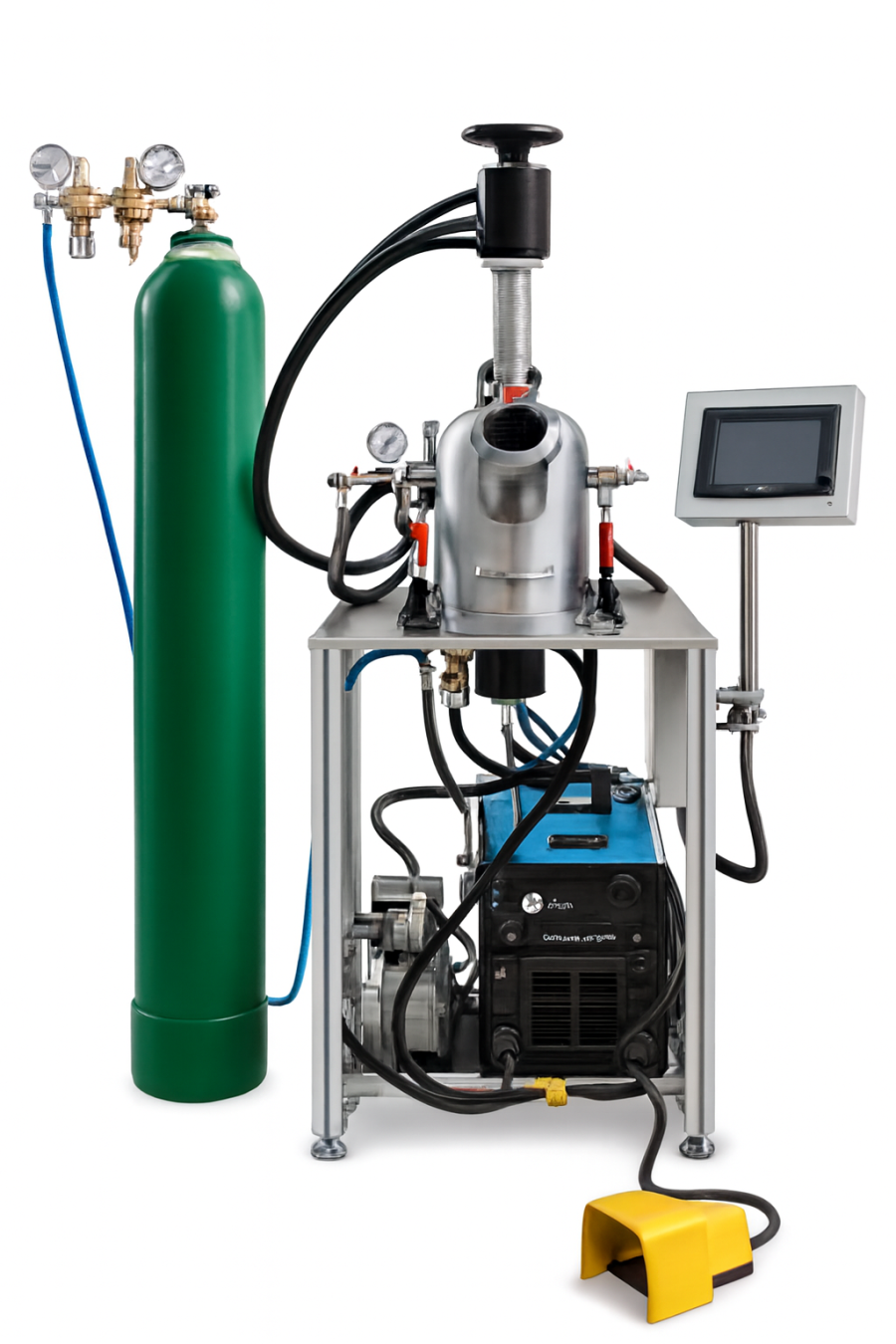

| Cihaz Marka ve Modeli | Laboratuvar ölçekli vakum ark ergitme cihazı |
| Ark Jeneratörü | Miller XMT 450 |
| Cihaz Türü | Vakum?nötr atmosfer şartlarında çalışan ark ergitme sistemi |
| Çalışma Sıcaklığı | 3500 °C'nin üzerinde (6332 °F) |
| Ergitme Haznesi (Kapasite) | 500 grama kadar bakır-krom alaşımlı ergitme haznesi |
| Basınç / Vakum Aralığı | 1×10?2 mBar ? 0,4 bar (opsiyon: 1×10?3 mBar ? 0,4 bar) |
| Atmosfer Kontrolü | PLC kontrollü otomatik basınçlı nötr gaz atmosfer kontrol sistemi |
| Soğutma Sistemi | Çift cidarlı (2×3 mm) su soğutmalı 304L vakum odası + debimetrelerle ayarlanabilir soğutma |
| Güç / Besleme | 815 A (600 A opsiyon) %25 çalışma döngüsü, 32,5 kVA 400 V / 50 Hz 3-faz şebeke |

C kalıbı
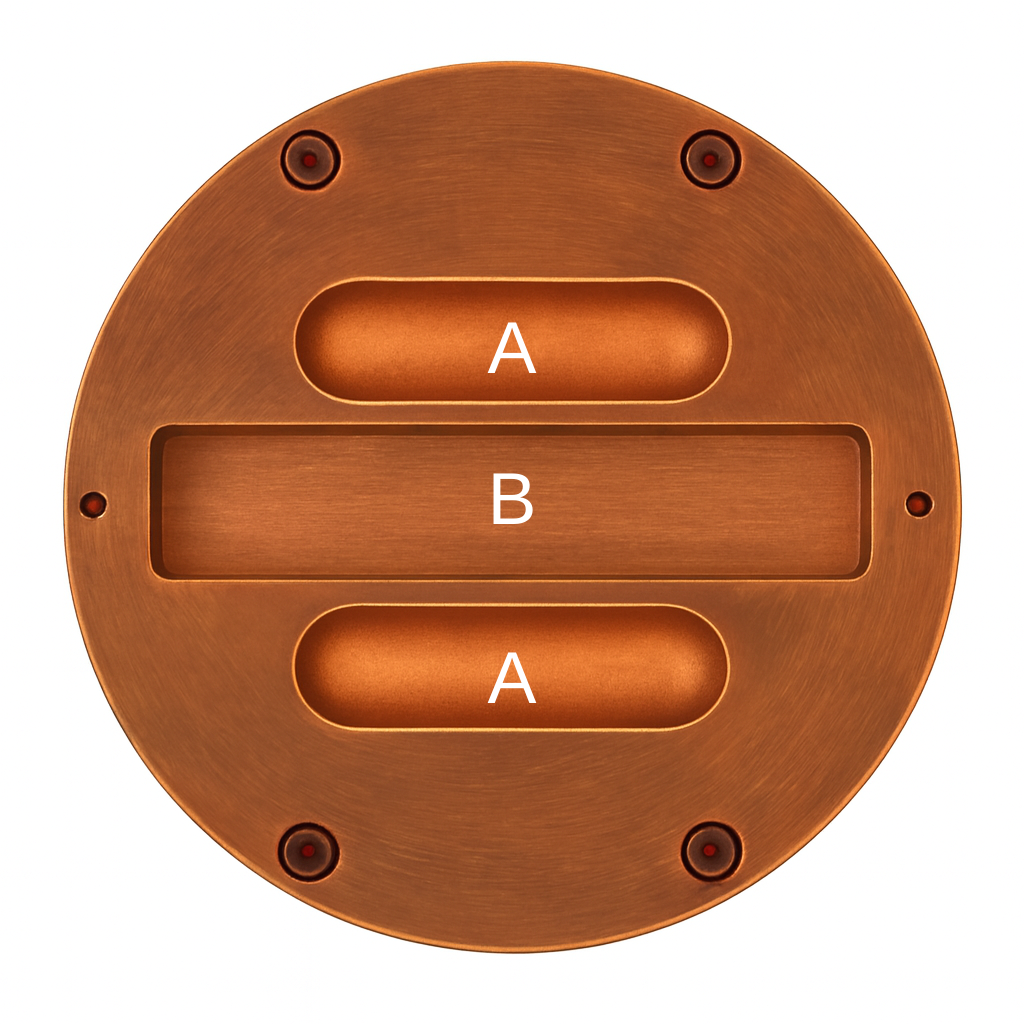
| Kalıp | Uzunluk | Genişlik / Çap | Derinlik | Not |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Kalıbı | 80 mm | 25 mm | 10 mm | En fazla 150 gram malzeme üretilebilir. |
| B Kalıbı | 155 mm | 40 mm | 15 mm | Kalıbın dolması için en az 200 gram malzeme gerekmektedir. |
| C Kalıbı | - | 70 mm | 20 mm | En fazla 150 gram malzeme üretilebilir. |
2025
In this study, the effects of Cu addition on the phase evolution, microstructure, and elemental distribution of Al1.5Co4CuxFe2Mn1.5 (x = 0, 0.1, 0.5, and 1.0) high-entropy alloys were systematically investigated. In addition, nanoindentation, magnetic properties, atomic force microscope, and magnetic force microscope analysis were carried out. XRD analysis revealed that some HEAs have BCC, FCC, and Laves phases. SEM and EDS images show that the alloys solidify in different ways depending on the Cu content, with grain structures becoming finer and secondary phases forming. Furthermore, it was revealed that the mechanical properties of the alloys change as the Cu content increases. The maximum Cu content (Cu10) peaked at 12.15 GPa nano hardness and 423.9 GPa elastic modulus. Magnetic saturation decreased and coercivity increased as the Cu content increased. The Cu0 alloy was found to have a saturation of 143 emu/g and a coercivity of 1.5 Oe. According to MFM analyses, as the Cu content increased, the ratio of the phase with high ferromagnetic interaction strength in the alloys decreased.
Keywords: High entropy alloys Magnetic properties Microstructure Phase structure Magnetic force microscope
2025
This study produced binary Mg-Ni and ternary Mg-Ni-Ag, Mg-Ni-Fe, and Mg-Ni-Ti alloys using vacuum arc melting and characterized. Binary Mg-Ni alloys were initially prepared, and their evaporation behaviors and structural properties were investigated. Significant evaporation losses were observed during melting due to Mg's low evaporation temperature, and the phase formations within the alloy were evaluated. Subsequently, ternary alloys were produced by adding different amounts of Ag, Fe, and Ti elements to the Mg-Ni binary alloy. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analyses revealed the formation of various phases, such as Ag17Mg54, and Ni3Ti as well as Mg, Mg2Ni, MgNi2 phases. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images demonstrated the distribution of these phases within the microstructure. Corrosion tests conducted through electrochemical measurements evaluated each alloy's corrosion potential (Ecorr) and corrosion current density (icorr) values.
Keywords: Mg-based alloys Structural properties Corrosion resistance Evaporation behavior
2024
The motivation for the present work is to explain the ferromagnetic properties of Cantor high entropy alloy by adding an alternative metal atom instead of Cr, which decomposes at high temperatures. With this motivation, MnTix and AlTix (x=0.0, 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5) were added to FeCoCuNi alloy to investigate the change in magnetic properties related to structural properties. The FeCoCuNiMn HEA showed similarities with the Cantor alloy, including an FCC phase. Replacing Mn with Al introduced B2 and BCC phases alongside FCC. Adding Ti to the FeCoCuNiMn alloy did not affect the phase structure but refined the microstructure. In contrast, Ti induced a transition from FCC to BCC in the FeCuCoNiAl alloy.
Keywords: High entropy alloys Magnetic properties Titanium effect
2024
This study investigated the microstructure and mechanical properties of the recycled Ti6Al4V alloy produced using the waste chips vacuum arc melting (VAM) process. The waste chips were cleaned to remove machining residues before VAM and dried in the oven. The dried and compressed chip compacts are vacuum arc melted and hot rolled. Microstructural characterization was performed by using an optical microscope, scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis.
Keywords: Ti6Al4V alloy Waste chip Recycling Vacuum arc melting (VAM) Mechanical properties
2024
This study aims to improve the structural strength of the commonly used Ti-15Zr alloy in dental applications by investigating the effects of low boron additions. Ti-15Zr alloys containing 1?4% boron have been produced by vacuum arc melting. The phase ratios in the microstructure of the produced alloys vary according to the boron content. With increasing boron content, the ratio of TiB compound in the phase structure increases.
Keywords: Ti-15Zr Boron Doping Vacuum Arc Melting Mechanical properties
2024
Recent research has heavily focused on high entropy alloys (HEAs) due to their promising potential for diverse industrial applications. This study investigates the CoCuFeNiNb alloy, analyzing its structural, tribological, and electrochemical characteristics. The alloy was synthesized using vacuum arc melting in an argon environment and was subsequently examined through X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), wear testing, and corrosion analysis. The results reveal that the alloy contains FCC, BCC, and Laves phases. In a 3.5 wt% NaCl solution, the alloy exhibited a corrosion potential of ?0.236 V and a corrosion current density of 1.89×10?5 A/cm2.
Keywords: High entropy alloy Vacuum arc melting Tribological properties Corrosion properties
2023
In the current study, a CoCrFeNiAl0.5Nb0.5 high entropy alloy was manufactured via arc melting and exposed to laser surface remelting. Both alloys are composed of four phases. Laser remelting did not change current phases, but it affected the microstructure. Hardness increased from 475 HV to 785 HV thanks to the change in phase ratios and grain refinement resulting from laser remelting. Wear resistance improved due to the increase in hardness, and volume losses decreased by 28%.
Keywords: High entropy alloys Laser Remelting CoCrFeNiAl0.5Nb0.5 Wear Corrosion Oxidation
2023
FeB-based alloys were successfully produced by the vacuum arc melting method. FeB-based alloys with various compositions were obtained by the gradual addition of different elements with Cu, Co, and Mo. The structural, magnetic, and electrochemical properties of the produced alloys were investigated. All FeB-based alloys demonstrated soft magnetic properties. The lowest coercivity was 13 Oe for the Fe85B15 alloy, and the highest saturation magnetization was 173 emu/g for the Fe63Co21Cu1B15 alloy.
Keywords: FeB-based alloys Electrochemical corrosion Magnetic properties Microstructure
2023
The formation of the Ti substituted Mg2Ni alloys, a promising hydrogen storage material for various applications is studied in detail. Mg1.95Ti0.05Ni alloy and ribbons are successfully prepared by vacuum arc melting and melt spinning methods. The phases, microstructures, and thermal behavior of the alloys and ribbons are characterized by XRD, SEM, TEM, DTA/TG. During the initial three cycles, Mg1.95Ti0.05Ni ribbons showed 2 wt% hydrogen storage capacity.
Keywords: Mg2Ni based Alloy Hydrogen storage Structural analysis Wien2k Density functional theory
2023
The fluxgate magnetometers have been used in many space missions due to their stability, low cost, low mass, and good measuring sensitivity and range. Proton irradiation was used to simulate space weather conditions near the Earth's magnetosphere in Van Allen belts. The effect of proton irradiation on the structural, magnetic, and sensor performance of our fluxgate sensors was studied with irradiation doses up to 60 kRad. Sensor's materials were prepared using a planar flow casting technique having two different compositions, namely Fe38Co38Mo8CuB15 (Fe38) and Fe42Co42CuB15 (Fe42).
Keywords: Fluxgate magnetometer Proton irradiation Sensor sensitivity Fe-based amorphous alloys
2023
Bu çalışmada klasik Cantor yüksek entropili alaşımın bileşiminde yer alan Mn yerine eklenen Cu elementinin mikroyapıda ve mekanik özellikler üzerindeki etkileri araştırılmıştır. CoCrFeNiMn ve CoCrFeNiCu yüksek entropili alaşımları ark ergitme ile üretilmişlerdir. CoCrFeNiMn alaşımın maksimum çekme gerilmesi 501 MPa iken CoCrFeNiCu alaşımının maksimum çekme gerilmesi 491 MPa olarak bulunmuştur.
Anahtar Kelimeler: Yüksek entropili alaşımlar Mikroyapı incelmesi Mekanik özellikler
2022
This study is dedicated to the detailed investigation of boronization kinetic, microstructural, mechanical, and wear properties of high entropy alloys (HEAs) considering their sluggish diffusion effect properties. A CoCrFeNiAl0.5Nb0.5 HEA was powder-pack boronized in the interval of 850?1050 °C for 2, 4, and 6 h. The wear losses have decreased due to the increase in hardness and an improvement of up to 99% has been achieved.
Keywords: High entropy alloys Boronizing Characterization Kinetic Fracture toughness Wear
2022
In this study, the effect of Ti addition on microstructure and corrosion properties of high entropy CoCuFeNiMnTix (x = 0.0?0.5) produced by the vacuum arc melting method was investigated. The corrosion resistance of the CoCuFeNiMnTix alloy decreased with the increase of Ti addition. Ti addition's most important effect on the CoCuFeNiMn alloy's corrosion properties was determined as the transformation of pitting corrosion type to galvanic corrosion.
Keywords: High entropy alloys Corrosion properties Ti addition effect
2021
In the present work, Al10Co24Cr10Fe15Ni34Ti6Cu1 (at.%) was obtained high entropy alloy (HEA) with vacuum arc melting. The microstructure, tribological properties, oxidation, and corrosion resistance of the HEA were detailly investigated. The faced-centered cubic solid solution structure was observed in the microstructure. The corrosion potential (Ecorr) and the corrosion current density (Icorr) values of the alloy were determined ?0.082 V and 2.18 × 10?8 A/cm2, respectively.
Keywords: High entropy alloys Microstructure Surface oxidation Tribological properties Corrosion resistance
7500 TL+ Sarf Giderleri ( KDV Dahil Değildir.)
Vakum Ark Ergitme (Arc Melting) cihazı, metal ve alaşımların kontrollü ortamda ergitilerek laboratuvar ölçeğinde üretilebilmesini sağlayan yüksek sıcaklık kapasiteli bir ergitme sistemidir. Çalışma prensibi, iki elektrot arasında oluşturulan elektrik arkı (ark plazması) ile çok yüksek enerji yoğunluğu elde edilmesine dayanır. Oluşan ark, numuneyi kısa sürede ergitir; bu sayede hızlı alaşım üretimi, kompozisyon denemeleri ve homojenleştirme amaçlı yeniden ergitme işlemleri verimli biçimde gerçekleştirilebilir.
Bu cihazların en önemli avantajlarından biri, ergitme işlemini vakum veya nötr gaz (ör. argon) atmosferi altında yürütebilmesidir. Böylece ergitme sırasında oksijen ve nem kaynaklı oksidasyon riski azaltılır; özellikle oksidasyona hassas metallerin işlenmesinde daha temiz ve tekrarlanabilir sonuçlar elde edilir. Sistemlerde genellikle vakum hattı, gaz besleme ve basınç kontrol ünitesi bulunur; bu altyapı sayesinde ortam koşulları proses boyunca kararlı tutulabilir.
Ergitme bölgesi çoğunlukla su soğutmalı bakır bir hazne üzerinde yer alır. Bakır haznenin yüksek ısı iletkenliği, hem ergitme yüzeyinin korunmasına hem de numunenin hızlı soğumasına katkı sağlar. Birçok uygulamada numune, homojenliği artırmak için birkaç kez çevrilip yeniden ergitilir. Böylelikle element dağılımı iyileşir ve daha tutarlı bir mikroyapı elde edilir.
Vakum ark ergitme cihazları; yeni alaşım geliştirme, ön ergitme/külçe hazırlama, araştırma amaçlı küçük ölçekli üretim ve belirli kompozisyonların hızlı şekilde denenmesi gibi alanlarda yaygın olarak kullanılır. İşlem parametreleri; vakum seviyesi, kullanılan inert gaz, ark akımı/gücü, ergitme süresi ve yeniden ergitme sayısı gibi değişkenlerle kontrol edilir. Bu nedenle cihaz, özellikle Ar-Ge çalışmalarında yüksek esneklik ve kısa çevrim süresi sağlayan güçlü bir ergitme yöntemidir.
05 Ocak 2026